Google News should be the focus of any digital media and content publisher, given the traffic it drives to news sites every month.
It’s been some years since Google last provided a news traffic analysis, but in 2020 it said it sent “Google users to news sites 24 billion times” every month. This equates to more than 9,000 clicks per second.
While ascribing a potential monetary value to these clicks is challenging, global financial consultancy Deloitte attempted to do just that in a 2019 study. The report, which Google has even cited, estimates the value of this traffic for large publishers (PDF download) at €0.04-0.06 ($0.04-0.06) per click.
Given the multitude of changes since its launch in 2002, however, ranking in Google News search results requires a greater degree of expertise and finesse than ever before. For publishers, that means staying abreast of, and applying, the most up-to-date search engine optimization (SEO) practices.
Read on to learn more about Google News SEO best practices and why they need to be at the forefront of every editorial strategy.
Table of Contents
What Is Google News?
Google News aggregates news articles from the last 30 days, clusters them by topic and displays them based on a user’s location, language settings and interests.
Articles from several sources around the same topic will be presented together without duplication. The purpose, as stated by Google, is “to help everyone understand the world by connecting people with high-quality news from a variety of perspectives”.
Google News, which was launched in beta in 2002 and officially in 2006, has undergone several evolutions. For example, the Full Coverage feature was launched as part of Google News in 2018 before being rolled out to Search on mobile phones in March 2021.
How Google News Works
Google’s news article rankings have been determined algorithmically ever since the launch of the Google News Publisher Center in 2019. Prior to this, publishers submitted their stories manually.
Google has outlined seven factors that determine its news rankings:
- Relevance: How relevant the story is to the user’s query.
- Location: Where the searcher’s located can choose the stories and news outlets they see.
- Prominence: The depth of coverage, how frequently other outlets cite a story and any original reporting.
- Authoritativeness: This is determined by feedback from Google’s Search Quality Raters of the perceived usefulness and reputation of a page, and backlinks from prominent websites.
- Freshness: New information on a current event has a higher chance of surfacing than older stories.
- Usability: A measurement of a website’s usability and accessibility, including its load speed and whether it uses responsive design and is cross-browser compatible.
- Interests: User-defined interests, coupled with their reading habits, will determine the content that appears on Google Discover and Google News’ “For you” section.
Is There a Best Article Length for Google News?
Google News doesn’t rank articles based on how long they are, only on the seven factors listed above.
This means that publishing a shorter article as quickly as possible on evolving stories is better than waiting to have “enough” detail. The news team can always update the story as new details emerge, maintaining that freshness edge.
Don’t worry, we’ll go into this in more detail in the Google News SEO Tactics section below.
Where Google News Appears
Google News comes in many shapes and sizes across both desktop and mobile platforms. News publishers have some influence over whether their content will appear on certain surfaces, while others are dictated by user personalization.
Before diving into this section it’s important to note that, unlike Search, Google News doesn’t solely rely on algorithms to surface news stories. It also depends on information provided by publishers within their own Publisher Center to feed into its news specific products.
We’ll dive into these two aspects in more detail later, but for now, let’s look at which Google News surfaces publishers can influence and which individual user settings shape directly.
News Surfaces That Favor Publisher SEO

News publishers can improve their chances of appearing on most Google News surfaces, including:
- News.google.com: This is Google News’ dedicated homepage.
- Google Search on browser: Google may show news results within its regular results rankings, though this is uncommon. Google is more likely to use either the News tab or one of its two dedicated news surfaces within the SERPs themselves.
- News tab: Google will show users full news coverage of a particular topic in this section. It’s accessible either by clicking the tab at the top of the SERP or the “More news” button at the bottom of the Top Stories SERP.
- Top Stories SERP feature: Google will show a collection of relevant stories at the top of a SERP when it determines a user’s query is news related.
- Local Stories SERP feature: Google’s newest surface collects and displays local news stories in response to relevant user queries.
- Google News App: The app aggregates, organizes and highlights international and local news. There are several sections the algorithm selects content for, meaning publishers can influence. These include:
- Headlines: This section collects and displays all the latest international, national and local news. Only one story on a particular topic will appear and users need to click the “Full coverage” button to see other publisher’s versions of the same story.
- Full coverage: This button appears under most of the stories in the app’s For you and Headlines sections and leads to a complete list of publishers with a report on that subject.
- Newsstand: The app version of Google News Showcase.
- Google News Showcase: Google licenses and displays stories within curated News Showcase panels that are accessed via the Google News and Google Discover mobile apps and news.google.com.
- Web Stories: Built on accelerated mobile pages (AMP) tech, web stories can appear in Search and Discover.
- Search Generative Experience (SGE): Google is integrating generative AI into Search. SGE pulls data from relevant web pages, including news stories, to answer user queries.
News Surfaces That Favor User Preferences
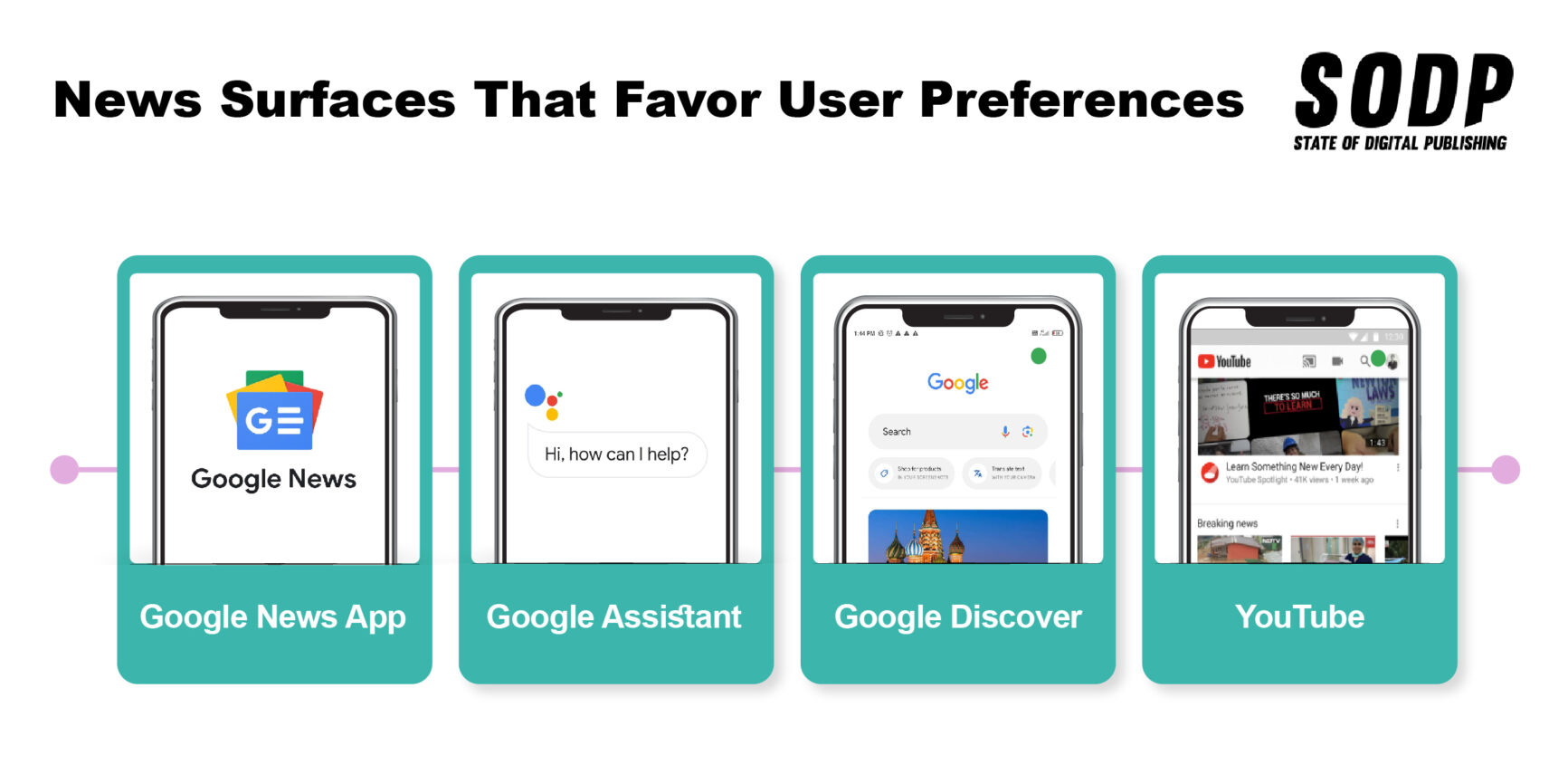
Unlike the above, algorithms customize what appears on the following surfaces in direct response to user preferences and behavior. These include:
- Google News App: The app also contains sections that user settings and browsing habits directly influence. These include:
- For you: This section delivers personalized news related to a user’s documented interests.
- Following: This section allows users to track topics, sources and locations while also saving searches and individual stories.
- Google Discover: Google’s mobile content recommendation engine has its own app, but users can also access it via the mobile Chrome browser.
- Google Assistant: This can provide up-to-date headlines and niche news stories.
- YouTube: In addition to a news section, it offers Breaking News and Top News shelves.
How to Appear in Google News
The State of Digital Publishing (SODP) team’s work with news publishers over the years has shown us that SEO practices can be roughly divided into two camps. These two camps represent the measurability of the actions publishers take toward improving SERP visibility.
In the picture below, the two camps have been color coded to simplify referencing.
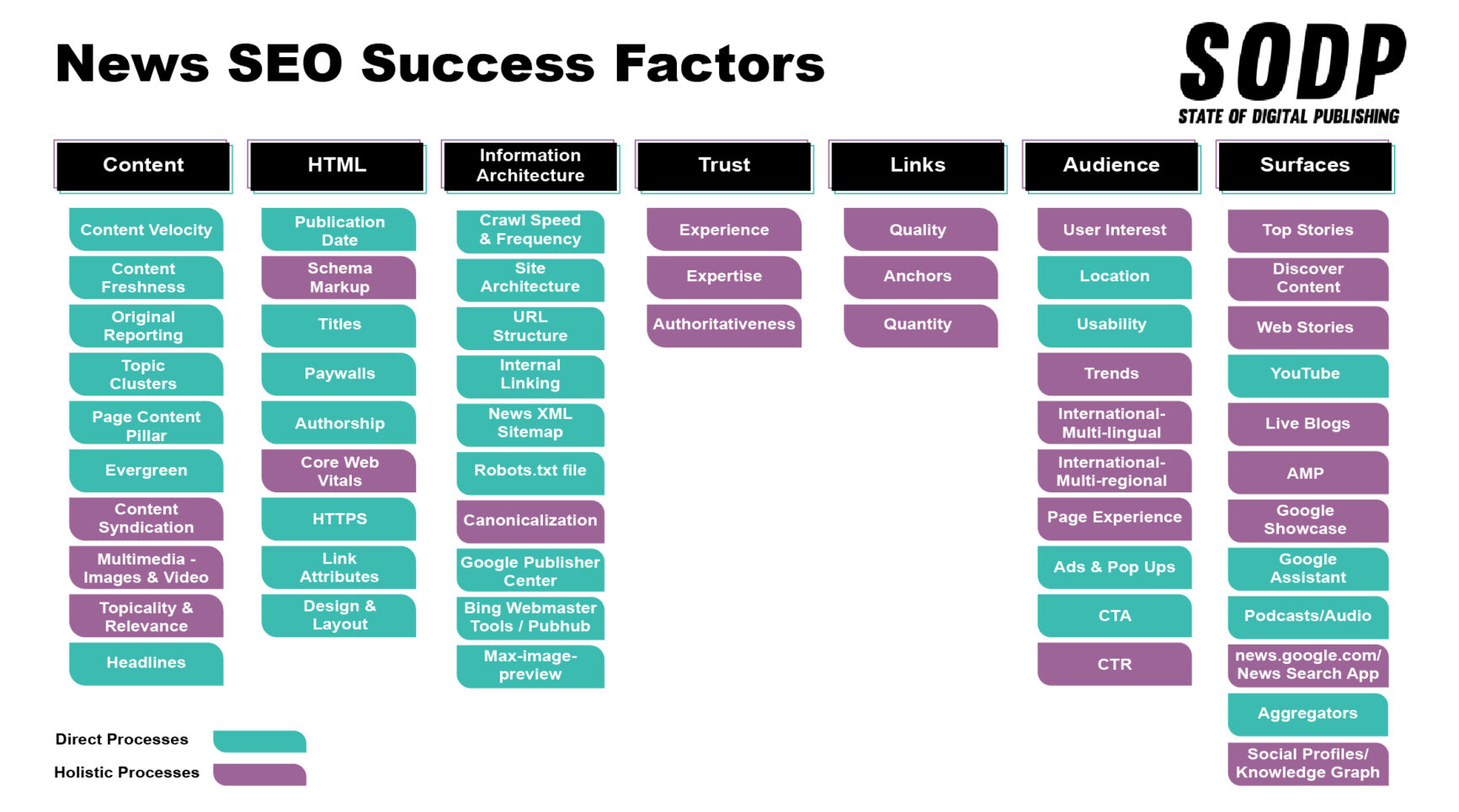
The items in aqua, which we refer to as “direct processes”, can lead to tangible results that are easily measured over a defined period of time. These are not “quick hits”, given the longer-term nature of the SEO process, but rather direct inputs that will yield measurable outputs.
Magenta items, or “holistic processes”, relate more to long-term brand building. Results from these processes are harder to measure over the short to mid term, but we’ve seen time and again that publishers who adopt them over the long term enjoy greater stability in terms of traffic and search engine visibility.
We’d absolutely recommend publishers start with aqua-colored items to build up both their confidence and their SEO fundamentals. However, long-term growth strategies must include magenta tasks to deliver sustainable results.
1. Follow Official Guidelines for Google News
The first step publishers need to take is to ensure that they’re adhering to Google’s content guidelines and technical guidelines.
These policies are pretty clear about what Google expects from news sites and include instructions such as publishing well-written and well-structured content and avoiding material types that the search giant will bar from news SERPs.
However, Google does have some more complex guidelines that are worth a closer look at.
Advertising and Paid Links
News sites should contain a reasonable and nonintrusive level of advertising and Google has made it clear that it will penalize sites trying to pass sponsored content as independent journalism.
Publishers must also block links that have been sold for ranking purposes or that otherwise violate Google’s guidelines about link schemes.
Duplicated and Syndicated Content
Publishers that duplicate or syndicate their content may run into some issues with Google incorrectly identifying which is the original story. This is a problem, given that Google will only show a single result for such content and may pick a clone.
When it comes to ensuring that Google correctly identifies the original versions of a story that either appears on the syndication partner’s website or a sister site, Google recommends adding one of the below robots meta tags to the article duplicate:
<meta name="Googlebot-News" content="noindex">
<meta name="Googlebot" content="noindex">The first stops Google News from displaying the story, while the second stops both Google News and Search from showing it to users.
Duplicated news content within a single site poses less of a risk to the publisher, with Google saying its algorithm will identify the “best version to show to users”. Still, there are steps available to those concerned, which include specifying a canonical URL.
Permanent Sections and URLs
Google recommends using permanent URLs for a site’s main news sections to ensure that Googlebot can crawl new content.
At the same time, publishers need to ensure they use HTML links for articles, as the crawler cannot follow image links or links embedded in JavaScript. Site owners should also avoid re-publishing pieces under a new URL.
Verify Robots.txt Settings
Verify that the robots.txt file, metatags or HTTP headers are not preventing Google from crawling article directory pages.
Language and Encoding
If a site has content in more than one language, different domains should be set up to avoid confusing Googlebot. To ensure the best results, websites should be encoded using UTF-8.
2. Conduct Technical SEO for Google News
Once publishers are comfortable that they’re complying with Google’s basic requirements, the next step is to begin implementing technical SEO across their domains. It’s essential to start with technical SEO because it is the foundation upon which everything else is built.
Design and Layout
Google is driven by a user-first philosophy, so if a site’s design leads to a poor user experience (UX), then it’ll likely struggle to improve its visibility.
Think in terms of satisfying user needs as quickly and simply as possible. One easy way to achieve this is by using semantic HTML tags to clearly define a page’s structure to web crawlers. The easier a page is to read and understand, the better its chance of ranking higher.
Ensure that articles can be rendered effectively in plain HTML and avoid using Javascript for rendering the article body or any links. Not only can Googlebot not index content in Javascript and follow site interlinks otherwise, but it’s also unable to follow image links, crawl PDFs and other formats besides HTML.
Code should be clean and well-structured and should be able to appear correctly in all browsers, devices and sizes. Present articles without interruptions, such as related article carousels or image galleries.
Arranging a new article’s elements in this order will also allow faster and easier crawling:
- Headline
- Image (with alt text)
- Author bio and date
- Article body
Learn more about Design and Layout

Site Architecture
Site architecture focuses on making it easier for users and Google to navigate through a site’s collected contents.
Without a competent site structure, navigation becomes much more complicated, disincentivizing users from returning. Using categories, tags, sections or any other custom taxonomy can make it easy for both users and Google to navigate the site.
Keeping the site structure as shallow as possible is ideal, as it will help to minimize the number of clicks needed to travel from the homepage to any other page on the site.
Numbered pagination is recommended in archive pages, as opposed to relying solely on previous and next buttons.
Learn more about Site Architecture

Page Experience
Google uses four page experience signals — Core Web Vitals (CWVs), mobile-friendliness, HTTPS and intrusive interstitial guidelines — to interpret and define a website’s UX.
These signals are an evaluation of site performance rather than content and serve as a tie-breaker when Google has to decide which news articles to show when each offers a similar level of coverage.
The four page experience signals are:
- Core web vitals (CWVs)
- Mobile-friendliness
- HTTPS
- No intrusive interstitials
These signals effectively boil down to how quickly a site loads, whether it is optimized for mobile use, is secure and avoids intrusive interstitial ads and dialogue boxes.
Learn more about Page Experience

Google News Sitemap
While having a separate Google News sitemap is not a ranking factor, it allows publishers to control the content they submit to Google News, improving Googlebot’s ability to discover and index sites more effectively.
Sitemaps should be limited to 1,000 URLs for articles published in the previous two days and should be updated as soon as new articles are published. Additional sitemaps can be created if the URL count exceeds 1,000, while a sitemap index file can be used to manage them all.
A Google News sitemap follows the standard sitemap XML schema but adds some specific Google News elements. Each included article URL has three mandatory tags:
<news:name>
<news:language>
<news:publication_date>
<news:title>
Once the sitemap has been created, it should be validated using an XML sitemap validator and submitted using Google Search Console (GSC).
Learn more about Google News Sitemap

Schema
Publishers can use schema markup, or structured data, to help crawlers more easily classify and display a page’s contents.
The main two types that publishers should focus on first are:
- Article
- NewsArticle
While Article schema is more widely used, meaning it is better documented and allows for easier maintenance of evergreen content in the long run, NewsArticle schema is increasingly being used for news and subscription content.
Publishers should also consider FAQ, fact check and author schema, which also make it clear to Google what a page’s content is. Structured data allows Google to display that page in rich-content format, increasing its chances of appearing as a rich snippet in Google Search results.
It’s important to understand that Google doesn’t require publishers to use schema to be eligible for Google News features such as Top stories. But it does help increase a story’s chances of appearing across various news surfaces, given that it more explicitly informs Google about said story’s content.
Publishers interested in schema should consider any schema that will add value to their content while matching the article’s intent.

Crawl Speed and Frequency
How often Google crawls a site is set algorithmically and depends on the publishing frequency. If several new articles are published each day, Google News will crawl more frequently to surface new content.
Once a new article has been discovered, the crawling bot will check for changes and updates to the story several times on the first day after discovery. After that, the crawling frequency will be significantly reduced. If there’s an error in an article that has already been fixed, it may take a while for Google News to show the updated version after that first day.
A web crawler will only crawl a site so many times, with this limit known as a crawl budget. The budget is set by two factors:
- Crawl limit: a site’s capacity and/or willingness to be crawled
- Crawl demand: more popular pages will need to be crawled more often.
Learn more about Crawl Speed and Frequency

Links to Sponsored and User-Generated Content
Google unveiled its new implementation of link attributes in September 2019. In addition to “nofollow”, there exist two other attributes — “sponsored” and “UGC”.
Sponsored is used to qualify links that are part of an advertising or sponsorship campaign. UGC stands for user-generated content. The attributes can be combined, so a link can be tagged as “nofollow UGC”.
Also of note is that Google treats the nofollow attribute as a recommendation rather than a directive for ranking purposes. This means that Google may indeed follow and crawl a nofollow link.
Learn more about Links to Sponsored and User-Generated Content

Google Publisher Center
Google’s Publisher Center allows publishers to submit content to Google News and then manage it.
Publishers can use the center to define details about their site — think RSS feeds, URLs and videos. While Publisher Center doesn’t have a direct impact on news search results, Google has said that using the tool will make it easier for the search giant to “index your site”.
Publisher Center allows publications to manage visual styles and designs, access new web traffic datasets, become eligible for the Google Newsstand and integrate Subscribe with Google (SwG).
Learn more about Google Publisher Center

Ad Best Practices
Many publishers rely solely on ads to monetize their content, meaning that having a best practices strategy is imperative.
Best practices can ensure that a site’s ads don’t interfere with Google’s crawlers while also boosting a site’s page load speed and general UX.
Some of these practices include:
- Only loading a single above-the-fold ad and in the viewport, preventing excessive ad density
- Use lazy loading for the rest
- Focus on the IAB’s most common ad unit sizes
- Use responsive ads to optimize ad sizing
- Making sure sites are mobile-friendly.
Learn more about Ad Best Practices

3. Content SEO for Google News
Next up, let’s look at how publishers can overhaul their content production process to boost their chances of appearing in Google News.
Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T)
Experience, expertise, authoritativeness and trustworthiness (E-E-A-T) are metrics used by Google’s Quality Search Raters when manually evaluating web pages.
Search raters are a team of 10,000 humans that rate search results to help fine-tune and improve search algorithms. Their new guidelines reinforce the idea of rewarding original reporting in search results.
Google has said E-E-A-T is technically a ranking factor, it has also said search raters’ reviews are used in its development of search engine updates.
There are no shortcuts here. Building trust requires a proven track record of publishing high-quality, engaging content that encourages users to click on and read. Trust is assigned for a specific topic and location and doesn’t translate to other topics. But how does Google assign trust?
It does so by analyzing search and traffic patterns, as well as the number of backlinks a site has attracted, along with their reputational quality. While social media is not inherently a factor, a sizable social media following probably correlates well with other trustworthiness indicators.
Learn more about Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness and Trust (E-E-A-T)

Develop Original Reporting
Google News took steps to reward original reporting in 2019 with higher ranking positions and SERP features. The move benefits news organizations that can be the first to cover a story.
Google will give visibility to original reporting with rich textual content along with other more comprehensive articles that were published later. The changes Google has made affect not just its algorithm but its search rater guidelines as well.
Google News prioritizes original content. If content is syndicated, scraped or rewritten from other sites, it won’t feature in Google News.
Taking this into consideration, publishers can benefit from several original reporting strategies:
- Speed of publishing: breaking news needs to be reported within the first 5-15 minutes.
- Linking: Link to older and/or relevant articles to build authority for news articles.
- Refresh headlines: Updates headlines as the body is updated.
- Reporting accuracy/transparency: Vet facts, figures and sources meticulously, then list them.
- Fresh perspectives: Approach a topic from a unique perspective.
Learn more about Develop Original Reporting

Content Freshness
The Google News algorithm tends to favor sites with a high content output, as this usually correlates with content freshness and authoritativeness.
It’s also logical that by publishing many stories daily, there is a greater chance of at least some of them surfacing in Google News.
Content freshness is the most important for:
- Trending content (e.g., breaking news)
- Pre-scheduled events (e.g., sports results)
- Seasonal content (e.g., Oscar winners)
- Evolving content (e.g., best-of lists)
While more recent, up-to-date articles have a higher chance of being presented in Google News, the personalization aspect of the platform means that some older stories can still surface.
Google’s algorithm will determine, depending on the topic, which is more useful to a user: a more recent, updated article or an older but more extensive article.
Learn more about Content Freshness

Topical Relevance
Apart from freshness, Google’s other main consideration when ranking an article is how relevant it is to the current search or a given news topic.
Publishers should use keyword research to understand what people are searching for, how many are looking for information, their preferred formats, their knowledge gaps and how well rivals are covering a topic.
This data paints a picture of what audiences are interested in and how extensively rival outlets are targeting the niche. At the same time, using appropriate keywords that are related to a topic will help to signal topical relevance to the subject matter.
There are plenty of tools that help with data gathering and analysis, which are essential steps before deciding which keywords to target.
Additional steps publishers can consider when trying to rank for any given topic include:
- Prominent placement: Publish plenty of articles on the same topic across the homepage and section pages and interlink them. These are strong signals of relevance.
- Topic clusters: A topic cluster helps search engines better understand the content’s relevance.
Learn more about Topical Relevance

Meta-Titles
Meta-titles tell crawlers what to display in the search results, meaning they are the first point of contact for many prospective readers. Getting the right title is crucial to determining search result placement as well as CTR.
While a publisher will set their own meta-title, Google News may decide to write its own title if it thinks its version is a better fit for the page’s content. To avoid any confusion, keep the title and the H1 the same.
It’s worth noting that publishers can set an article headline within the Article schema, which has seen its hard character limit of 110 removed. While the only penalty for lengthy headlines is that they might be truncated within Google, we’d advise against larger character counts as such headlines are unlikely to capture reader interest.
Best practices include:
- Titles no longer than 60 characters
- Use sentence case or title case.
- Create unique titles for every story
- Be descriptive
- Avoid keyword stuffing
- Avoid ambiguity
Learn more about Title and Headlines

<title> tags are, why they’re important, how to write a good title tag and the most common issues to avoid when trying to create SEO titles and headlines.Dates
Don’t include more than one date on a page. In our experience, including more than one date on a page — such as the publication date of articles in section pages — can confuse Googlebot.
Publication dates should be placed between the article’s title and text. When using a sitemap, verify that the dates have been provided correctly in Google Search Console. Otherwise, the articles won’t show in Google News.
An article can be given a new date and time following an extensive update or the addition of significant information.
Don’t try to game the system by rewriting a story and updating the publication date without adding significant new information. Google will flag this, and the content won’t be picked up.

Video Content
Google is increasingly showing video content in both traditional search results as well as Google News and Top Stories.
It’s important to ensure that embedded videos have relevant keywords in the title, description and time stamps in order for Google’s algorithm to pick them up.
Organizations with a strong focus on video content should submit a YouTube video channel to Google News. They’ll need to first have a site already approved in Google News before submitting a YouTube channel for approval.
Learn more about Video Content

Image Optimization
Google News displays images within articles as long as they’re relevant to the story. Images need to be placed after the article title and before the date and article text and should have well-written and relevant captions and alt-text.
Use structured data — schema.org or Open Graph protocol — to tell Google News which is the main image for use as a search results thumbnail.
Remember, the Google News crawler won’t follow any image links. If Google News isn’t picking up an article’s lead image, then check that:
Content from our partners
- Images have a minimum size of 60×90 pixels.
- They are hosted in the same domain as the article.
- The image ratio (height and width) is reasonable.
- Standard image formats — such as BMP, GIF, JPEG, PNG, WebP, and SVG — have been used.
- The robots.txt file or a meta tag isn’t blocking the crawler’s access to the image.
Learn more about Image Optimization

Backlinks and Internal Links
Because Google News values fresh coverage of current events, the classic SEO strategy of building backlinks over a long time period won’t work here.
Instead, focus on building overall site trustworthiness over time and that means, among other things, backlinks to the main site.
In the short term, however, the only winning strategy is to be the first to break news on any given topic or event. If other publishers link and reference an article, it’s an indicator to Google that the piece is the original and most authoritative source on the topic.
While building backlinks for news stories is more complicated than for evergreen content, internal linking strategies remain the same.
Use internal links, where possible, to transfer some of the link equity from high-traffic, authoritative pages to news articles.
Learn more about Backlinks and Internal Links

Location-Based SEO
Some articles will rank higher for some users based on their location. Local events and stories will surface more easily to local users.
This means that a local news site could, for example, rank higher than the New York Times for a local news story. This strategy is, by its nature, more relevant for smaller publishers and takes already existing best practices and refocuses them through a local news coverage lens.
For example, local publishers need to:
- Research keywords for local content
- Write original local content
- Update that content regularly
Being a local publisher is not enough without any of the earlier fundamentals we’ve already discussed.
Learn more about Location-Based SEO

4. Google News SEO Tactics
Consistently appearing in Google News can feel like a daunting challenge at first, but this list of tactics that the biggest news sites in the world have pioneered to drive Google News traffic their way.
Speed of Coverage
Ranking for a breaking news story is an extremely competitive affair and requires rapid coverage of the story.
Speed of coverage is key, rather than comprehensiveness. Once a story has received accurate initial coverage and has been picked up by Google News, only then should publishers worry about fleshing out their coverage.
Even if a story misses the initial Google News round-up, publishers can continue to update it in real-time to challenge those competitors that have made an appearance.
Publisher Velocity
Publisher velocity focuses on increasing the amount of quality content published over time in order to grow a site’s organic traffic and audience.
How often should a publisher provide fresh content? While there’s no hard answer to this question, a good place to start figuring this out is with an analysis of the competition. Scaling up publication schedules is resource-intensive, so understanding the competitive landscape is essential to maximizing return on investment (RoI) in content production.
The next steps involve planning content in advance wherever and whenever possible — government sessions, sports results, cultural events, planned protests, etc — as well as repurposing and refreshing existing content.
Learn more about Publisher Velocity

Pillar Cluster Strategy
The pillar cluster strategy is more commonly used in evergreen publishing to help build topical authority within a specific niche. It can, however, be used within the news space.
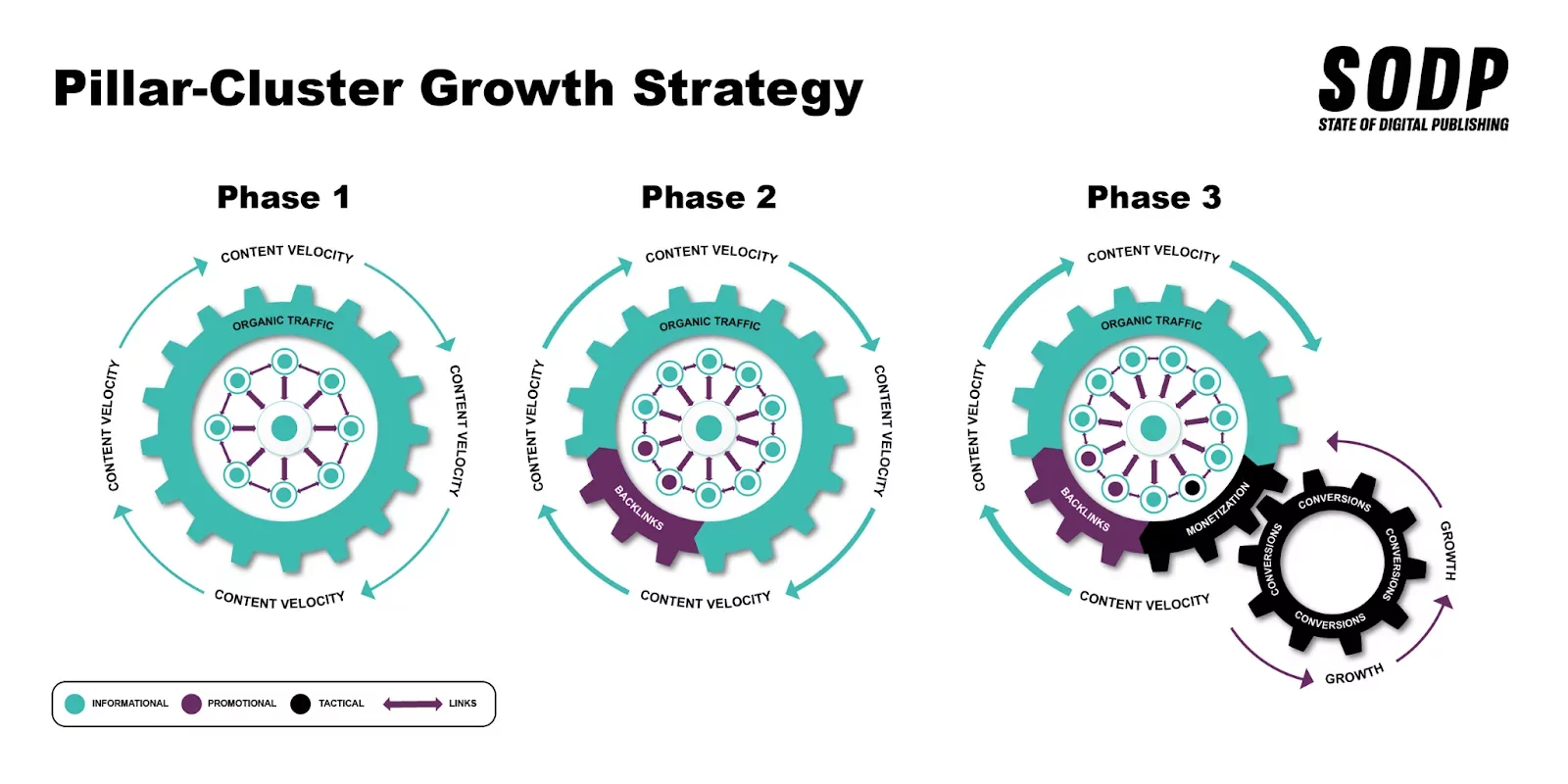
Typically a pillar page covers a topic in-depth and links to cluster content. For example, a pillar page might be a city with supporting cluster content being the best restaurants or attractions in that city.
This approach doesn’t work with breaking news coverage, where speed is key to appearing within Google News. However, a variation of this approach was briefly covered in the above section about internal links.
News publishers need to treat the original news article as a pillar page that links to and from relevant content. This content can either be created new or is a refresh of existing material. The strategy works best when the cluster content is created in concert with the original content. Resource and time constraints will make refreshing and repurposing existing content easier than writing and publishing new articles.
Learn more about Content Clusters

Google Trends
Google Trends is a useful tool for understanding historical audience interest in recurring events, such as sports finals, shopping events and international celebration days.
While Google Trends may, at first glance, restrict data to a single day, there are ways to get a more granular view of historical search activity when searching beyond the last seven days. This can be done by modifying the URL parameters.
Publishers should focus on looking for seasonal trends to better plan their news coverage of events. Doing so will allow them to update pre-existing content rather than writing something from scratch.
Google Trends also has a Related Queries function that provides insight into longtail keywords of interest. By focusing on longtail stories on a particular subject, news sites can build topical authority and compete for Top Stories inclusion.
More than this, however, topical authority in these subjects will allow publishers to compete during breaking news events.
Learn more about Google Trends

Google’s Training Resources
We thought it worth highlighting the additional resources Google has created to help news publishers improve their content’s discoverability.
The search engine giant has developed more than 50 lessons and video tutorials that cover three themes:
- Audience development: These courses share insight on Google’s core product suite (Google Search, Google Analytics, etc.), news industry tech, and engagement distribution best practices.
- Revenue growth: These sessions focus on building a sustainable business model using ad revenue and paywalls.
Digital journalism training: Google’s third set of courses focus on developing editorial teams’ digital skill sets and includes training on digital reporting, new storytelling formats and how to fight misinformation. The focus on fighting misinformation builds on Google previous efforts to help its users more easily spot misinformation.
Final Thoughts
Publishers that consistently place at or near the top of Google News will see their traffic soar. Besides traffic from Google News, publishers can also benefit from prominent placement in news-related Search results through SERP features as well as on app-based surfaces.
These outcomes create new opportunities for news sites to boost ad revenue and/or convert visitors into subscribers. Even for publishers focused on a niche area, the benefits of optimizing content for Google News can provide great rewards.
With that in mind, we’ll continue to monitor the impact that newer surfaces, such as SGE, have on the Google News landscape. Understandably, there is a great deal of publisher concern over the impact that a Search-integrated large language model (LLM) such as Bard might have on CTRs.
For publishers looking to manage the process in-house, the SODP team has created a comprehensive Publisher SEO course that goes over every step discussed here and more in far greater detail. The course covers 55 modules and serves as a complete guide, with practical examples as well as detailed walkthroughs.
Publishers that are looking for help in managing this process can connect with our team of SEO consultants to request a free strategy audit.
There isn’t a shortcut to success here, but any publisher that wants to feature in the Google News results can do just that.

Related Stories: