17 Best Digital Publishing Platforms in 2024
Top Picks
Disclaimer: Our top picks are based on our editors’ independent research, analysis, and/or hands-on testing.
Ask ChatGPT
With readers increasingly switching to consuming content online, publishers need to constantly evaluate whether their digital publishing platforms are helping them stay competitive.
With more than 64% of the world’s population consuming digital content in some form, the strategic importance of digital publishing is undeniable. Publishers are, however, facing increased competition for that audience.
Traditional print-first models have increasingly shifted to a digital-first approach. For example, of the New York Times’ 9.7 million subscribers around two-thirds are digital-only consumers. This is digital darwinism at work — businesses either adapt quickly to disruptive technologies or vanish.
Digital publishing platforms are at the heart of this transition, enabling the publishing of everything from news and evergreen articles to ebooks and white papers. An online publishing platform offers various services and functionalities, such as creating digital magazines, customizing and branding digital content, SEO tools, e-commerce solutions, providing multimedia content creation, integrating ads for additional revenue, and managing subscriptions.
What Is a Digital Publishing Platform?
A digital publishing platform is a piece of software that enables publishers to produce, edit and publish content online via one or many digital channels. An online publishing platform offers various features such as creating digital magazines, customizing content, and integrating ads for additional revenue. A tweet or a podcast is as much a digital publication as the digital edition of the Encyclopedia Britannica.
Traditionally, the term digital publishing has been most commonly associated with the web-based publishing of ebooks, reports, digital magazines, catalogs, flipbooks, etc. These could either originate in digital form or be converted from a physical format to digital.
Most digital publishing software help publishers drive traffic and track analytics. This means a legacy magazine publisher, such as Good Housekeeping, can use a digital publishing platform to create online editions that are as rich and immersive as the print versions while also being able to leverage the platform to promote the digital magazine.
How Do Digital Publishing Platforms Work?
A digital publishing platform supplies automated tools that allow individuals and businesses to produce, publish and distribute digital content. An online publishing platform provides tools for creating, publishing, and distributing content, as well as managing subscriptions and integrating multimedia content.
Most publishing platforms run on a subscription model. Once publishers create an account and subscribe to a plan, the platforms provide them with the necessary tools to compile and design their content. A single content template can be used to create content across multiple formats such as ebooks, flipbooks, white papers or reports.
A digital publishing platform also allows publishers to distribute their content online across numerous channels, a practice known as multi-platform publishing.
For example, The New Yorker is known for its satirical cartoons that have been a distinguishing element of its carefully curated brand identity over the roughly 100 years of its existence. Cartoons in fact, became so central to The New Yorker that it was often described as the “best magazine in the world for people who cannot read”. But in 2020 it branched into creating and selling audiobooks of its print editions.
How to Pick the Best Digital Publishing Platform
Choosing the right digital publishing platform can be a daunting task, especially with so many options available in the market. An online publishing platform should offer features like SEO tools, e-commerce solutions, and multimedia content creation. Here are some key criteria to consider when filtering the options:
- User-Friendliness: How easy is it to use the platform, both for publishers and readers?
- Customization: Can publishers customize the look and feel of their content, including branding, design and layout?
- Distribution: How does the platform help with the distribution and promotion of content across various channels?
- Pricing: What are the costs associated with using the platform, including any fees or revenue sharing?
- Analytics: Does the platform provide detailed analytics and insights on content performance?
- Integration: Can the platform integrate with other tools or services, such as social media or email marketing?
- SEO tools: Does it help publishers in enhancing their content’s performance in the search engine rankings pages (SERPS)?
- Multilingual support: Does the platform streamline the release of content in multiple languages?
- Embedded content: Does it allow for the inclusion of videos, images, links and interactive elements?
- Payment gateways: Can publishers use paywalls to charge for premium content?
Digital Publishing Platforms vs CMSs
Digital publishing platforms share similarities with content management systems (CMSs). After all, both a digital publishing platform and a CMS deal with producing and sharing digital content. An online publishing platform offers specialized tools for creating and distributing digital content, unlike a traditional CMS.
A CMS is primarily designed for managing content on a website. It allows users to create, edit, and publish content, as well as manage the layout and design of the website. CMSs are typically used by businesses, organizations and individuals to create and maintain websites that are updated frequently. Popular CMSs are Joomla and Drupal.
Digital publishing platforms, on the other hand, are designed specifically for creating and publishing digital content such as ebooks, digital magazines and interactive content. They offer tools for designing layouts, adding multimedia elements and publishing content to multiple channels such as websites, social media and mobile apps. Popular platforms include Joomag, Issuu and FlipHTML5.
It’s worth remembering that these are not rigorous definitions and the line between the two systems can become blurred.
WordPress, for example, is typically thought of as a CMS used for building websites and blogs. However, adding the Paperlit plugin to WordPress allows users to convert their blog posts on WordPress to digital magazines.
At the end of the day, the difference amounts to a matter of specialization, even if the two might have some overlapping capabilities. Our first choice for creating a flipbook wouldn’t be WordPress, while Joomag isn’t our first pick for creating a blog post.
Adobe Experience Manager
Adobe Experience Manager (AEM) is an advanced CMS platform that is highly effective for digital publishing. It’s ideal for businesses looking to deliver interactive content to their customers through as many online touch points as possible.
Adobe Experience Manager helps to create, manage, optimize and deliver content in all forms effectively across all digital channels. By Adobe’s own estimates, switching to AEM has helped teams become 23% more productive.
The platform allows users to build and publish websites, branded apps and other interactive digital content. With Adobe Experience Manager, digital publishers can bring their content management system and digital asset management together and integrate them into the Adobe Creative Cloud.
- Well-designed digital asset management
- Easy collaboration between authors and editors
- Adobe Experience Cloud integrated
- Automatic adaptation to changing audience behavior
- Built-in workflows connect Adobe’s Creative Cloud to AEM
- User-friendly CMS offering easy editing and drag-and-drop functionality
- Flexible enough to support various digital business models
- Expensive for small businesses or organizations with limited budgets
- Customization may require specialized expertise and resources
Storychief
StoryChief can help teams and businesses that frequently produce and post content on the web save time, as it includes a built-in editorial approval flow and SEO.
Publishers can use StoryChief to help speed up the content creation process on existing CMS systems, such as WordPress and Adobe AEM, by taking care of complex processes.
However, it might not be the best fit for creating and distributing online flipbooks.
- Single-click publish to all channels
- Layout automatically adapts to the main website
- Pre-schedule features for publication and promotion
- Editorial planning tools
- Performance mapping across all channels in one dashboard
- Easy to use platform for non-technical team members
- Easy channel integration with CMSs such as WordPress and Webflow
- Limited design customization options
- The workflow automation feature can be inconsistent at times
WordPress
WordPress is a content management system (CMS) that can also double as an affordable and easy-to-use digital publishing platform. It’s a popular tool, powering more than 43% of all websites.
WordPress provides its users with effective tools for designing, publishing, performance tracking and content storage. The platform is ideal for publishers looking to build their audience base through regular release of interactive publications, such as online articles, blogs, video content, etc.
The platform might not be perfect for publishers looking to create and distribute online magazines and ebooks. Businesses looking to grow or reach a wider audience with effective content marketing strategies can benefit from this platform.
- Interactive content support
- Drag-and-drop editing
- Built-in social sharing features
- In-depth statistics with visual analytics
- Built-in SEO tools.
- Easy to set up and configure
- User-friendly tools that require minimal tech knowledge
- Security vulnerabilities due to its popularity and open-source nature
- Need for regular updates and maintenance to ensure optimal performance
- Limited customization options without coding knowledge or paid plugins/themes
FlipHTML5
FlipHTML5 is a publishing and subscription platform created for businesses looking to create digital flipbooks.
The digital magazine publishing platform allows administrators to store publications and manage and sell subscriptions on a unified interface. Visitors can read online and also download a publisher’s creation.
The platform might be the right fit for outfits looking to create, share and incorporate digitized content in their marketing activities.
- Batch conversion functionality to convert multiple PDF files into digital catalogs
- Custom domains and homepage banners
- Online flipbooks sales and payment collection facility
- Optical character recognition (OCR) feature for quick extraction of texts from images in multiple languages.
- Easy flipbook sharing features across various social platforms
- Data visualization across key statistics such as page visits, reads and shares
- Inability to import audio and video files directly into publications
- Higher pricing plans may not be cost-effective for small businesses or individuals
Flipsnack
Flipsnack is another digital magazine publishing platform ideal for transforming long-form content into flipbooks or online magazines.
The platform allows digital magazine publishers to edit and convert their PDF files into an interactive publication, providing user-friendly tools that require limited technical knowledge.
Additionally, Flipsnack comes with advanced tools that protect projects from being accidentally moved or modified.
- Simultaneous editing of several project elements
- Advanced content creation and management tools
- Online design studio to create and post online publications from scratch
- Virtual shelves to store digital magazines, ebooks and catalogs
- Real-time reporting tools
- Scheduling tools
- Automated tools to instantly turn a PDF file into a digital magazine
- Large library of templates
- User interface can be somewhat confusing for beginners
- Customer support can be slow to respond at times
Issuu
Issuu is a digital magazine publishing software that serves both publishers and individual users and is ideal for those looking to provide a great reading experience.
Apart from allowing publishers to create digital magazines and share their content, the platform also encourages visitors to sign up and browse publications. Readers can either choose to engage with free content or buy magazines and subscriptions.
Additionally, Issuu also provides effective tools to help its users to edit their images, PDF, text or any other form of content and share them across websites and social media platforms. The tools include features that allow designers to embed magazines, personalized guides and marketing catalogs on their websites and then optimize content to improve search engine rankings.
The platform has helped launch more than 30 million publications and is visited by more than 100 million unique visitors.
- Custom reading experiences for audiences
- Various third-party system integrations
- In-built project management feature to help track task status and delegate tasks
- In-depth analytics
- Easy content transformation tools
- Easy audience behavior monitoring
- Issuu’s free plan has limited features
Joomag
Joomag offers an all-in-one digital publishing solution for publishers looking to create, distribute, track and monetize their content from a central platform.
The platform is ideal for businesses looking to distribute their content across their audience base in different channels. Furthermore, it offers its clientbase of more than 500,000 businesses — which includes the likes of Men’s Health and Cosmopolitan — access to its online only Crater Editor interface.
- Interactive digital content in various formats and categories
- A huge number of predesigned templates for easy e-publishing
- Lead generation and management solutions
- Multichannel distribution solutions
- Easy-to-use online editor
- Comprehensive content analytics
- No option for offline access
- Pricing plans can be expensive for small businesses or individuals
Magloft

MagLoft features a simple interface that easily converts PDFs to interactive digital content, while also providing a platform to create ready-to-publish content from scratch.
Once users sign up with the platform, they can choose customized design apps for iOS, Android and desktop. They can then design and publish a magazine.
The platform offers a free trial so users can see a finalized version of their digital publication. However, they will need to subscribe to a plan to publish that product.
- Drag-and-drop content editor
- Live preview
- Built-in payment gateway
- Built-in CRM
- Custom subscriptions
- Advanced analytics
- Embed and share feature
- No support for PayPal
PressPad
PressPad is a digital publishing platform that offers three highly specialized services — digital magazine creation, mobile apps for news publishers and digital kiosks that enable publishers to sell PDFs from their own website without redirecting the consumer to a third-party seller.
The most remarkable feature of PressPad, and one which sets it apart from other digital publishing solutions, is that it allows publishers complete control over the entire production lifecycle of their publication.
From design and creation of their digital magazine and its accompanying app to selling it on their website through an embeddable kiosk, PressPad allows small publishers to compete on a level playing field.
PressPad also allows publishers to create their own magazine apps using nothing except the PDF files of their magazine. The app becomes available for download from the App Store or Google Play within seven days.
- Create an online newsstand that can be embedded on website
- Provides expert marketing support for increasing sales
- Build a branded mobile app without coding knowledge
- Allows easy integration with all major payment gateways
- Unlimited hosting for storing PDFs
- Easy integration with social media
- May not suit publishers looking for extensive customization options
- No free plan
Twipe
Twipe is an award winning SaaS-enabled solutions provider to digital publishers, with a special focus on newspapers and news magazines.
It is a two-time recipient of the Google-backed Digital News Initiative’s Innovation Fund which rewards technological innovation in quality journalism. And for good reason.
Twipe’s futuristic AI-powered digital assistant called JAMES sends personalized reading recommendations to readers based on an algorithm that blends each reader’s individual preferences with trending news stories. Tests of the software by UK daily The Times resulted in an up to 49% reduction in subscriber churn and a reader engagement rate of up to 70%.
Twipe also provides two advanced solutions to meet different needs of digital publishers — the Replica platform for creating interactive ePapers and the NextGen platform for interactive mobile-friendly editions of newspapers and magazines.
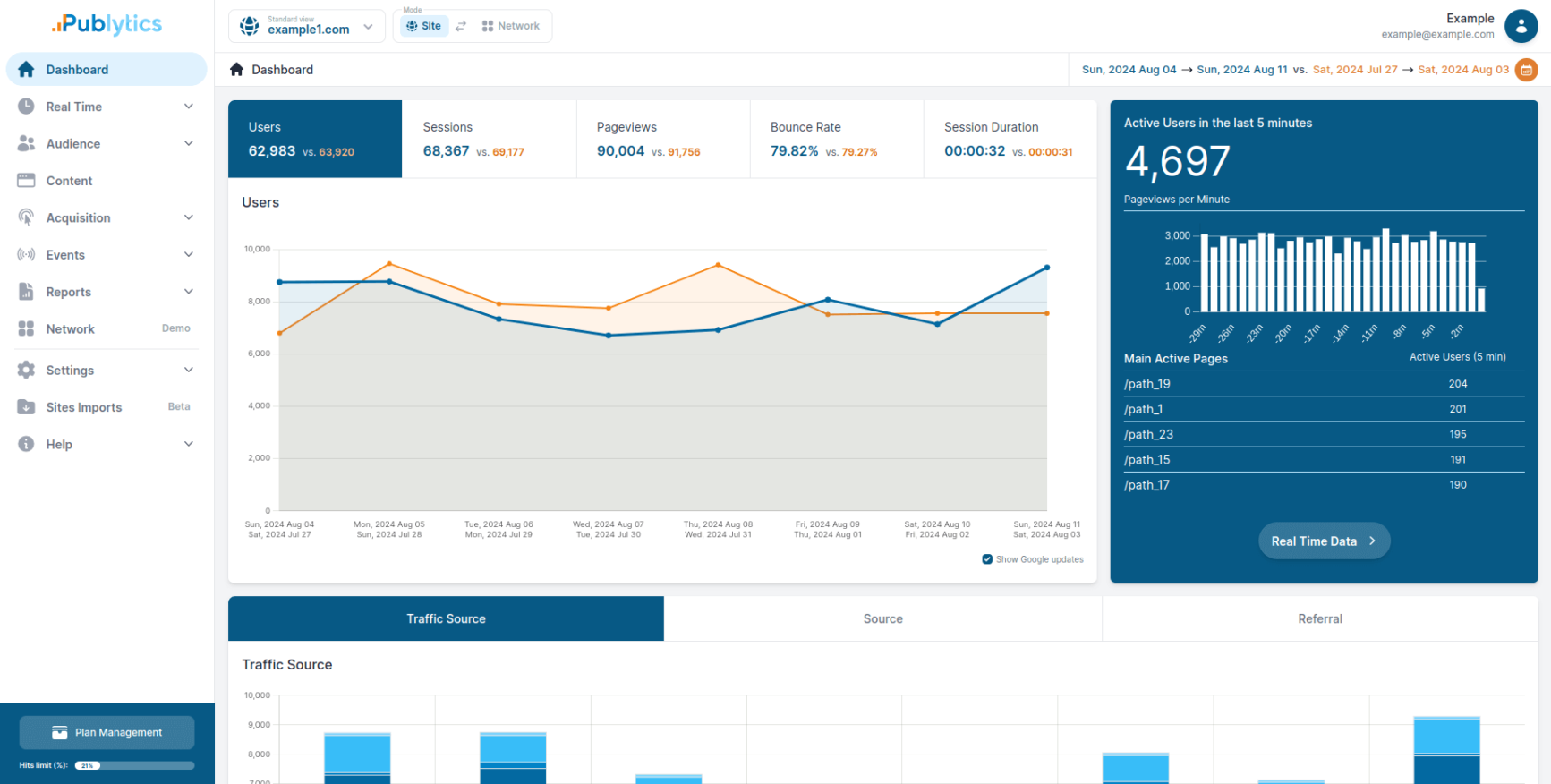
Its Engage platform equips newsrooms with advanced analytics tools to monitor the performance of their publications in real time.
Little wonder, then, that Twipe is trusted by some of the leading newspapers in the world including The Times and Le Monde.
- Easy SDK integration with e-papers across all platforms
- Personalized reading recommendations for readers
- Create interactive, fully touch-enabled ePapers
- Stylized article lightboxes
- Allows cross-platform digital publishing
- Advanced analytics that show real-time edition performance
- Limited customization options
Yumpu
Yumpu is a digital magazine publishing software that helps digital magazine publishers create, publish and distribute digital materials online.
The platform supports multiple forms of content such as text, images, audio and video, allowing publishers to integrate all types of content in their digital publications.
Yumpu allows a simple process of uploading a PDF and converting it into a Google-accessible, SEO-friendly digital magazine for its users. It allows users not only to digitize their publications but also increase the search engine relevance of their content.
The platform is ideal for magazine publishers looking to convert their long-form content into SEO-friendly digital magazines or books.
- Offline access
- SEO tools
- Third-party integrations
- Assistance and training
- Detailed analytics
- Lack of customization options
- Limited integrations
BlueToad
Founded in 2007, BlueToad is one of the oldest digital publishing platforms around. In the more than decade and a half since, BlueToad has grown to become one of the most trusted digital partners of publishers worldwide, publishing 130 million pages of content every month.
BlueToad provides the complete range of digital publishing services, helping publishers create interactive ebooks, flipbooks, digital magazines and everything in between. However, what makes BlueToad stand out from the crowd is its ability to create interactive, mobile-friendly editions of digital content with very little input.
With BlueToad, publishers don’t need to provide a PDF of their content and can simply use the platform to drag and drop images, videos and text and BlueToad then converts it into a mobile-responsive digital edition.
- Integration with third-party analytics and marketing tools
- ADA and WCAG compliant, meaning content is easily accessible to people with disabilities
- Allows publishers to use their color, design and font across all content and social media channels
- Provides phone, chat and email customer support, in addition to video tutorials
- Offers paywalls and subscriptions, digital ads and ad manager integration
- User-friendly platform
- Advanced analytics and tracking tools
- Doesn’t offer as many customization options as some other platforms
DCatalog

DCatalog offers a simple digital publishing solution for businesses looking to distribute their long-form content, such as ebooks, digital magazines, catalogs, emanuals, etc. The software features multiple templates for varied use cases.
Users can create an account, upload their material and design participative online content through a relatively simple process. They can then easily distribute the content through different channels.
- Choice of numerous templates
- Sharing and distribution features
- SEO profiles
- Archived editions
- Rich media management
- In-publication purchase
- User-friendly editing interface
- Social media integration
- Comprehensive reading experience
- Requires some technical expertise to set up and use effectively
- No free trial
- May not suit publishers looking for extensive customization options
Kitaboo
Kitaboo is a cloud-based platform that allows publishers to create, publish and distribute ebooks securely. Kitaboo also provides an eReader for an immersive reading experience and an eBookstore for publishers to sell their content.
Kitaboo is a niche publishing platform that focuses on creating text books for schools and colleges, and learning content for enterprises. Its partners include Oxford University Press, McGraw Hill and Pearson Education.
It stands out from the competition with its twin focus on security and creating interactive content. Its DRM-enabled ebooks offer best-in-class safety from online piracy, while its interactive content allows teachers and learners to interact via notes and suggestions within the content.
- Advanced security encrypted platform
- Allows multimedia integration into content
- Interactive dashboard provides data-driven insights for users
- Cross-platform functionality
- Easy content distribution using the Kitaboo eBookstore
- Easy integration with client website using Kitaboo SDK
- Copyright infringements are virtually impossible
- Relatively high pricing compared to some other platforms
- Limited third-party integration options
Quark
Founded in 1981, Quark is a specialized digital publishing platform that provides solutions targeted at medium to large scale enterprises.
Its flagship product, QuarkXpress, was first released in 1987 and continues to be popular among enterprises for producing digital marketing collateral such as flyers, catalogs and digital magazines. Newer versions of QuarkXpress include support for creating interactive ebooks and mobile apps as well.
Quark automates every stage of content creation, including collaboration, assembly, publishing and analysis through its advanced toolset.This helps businesses to automate and manage the content pipeline while also taking care of marketing and sales activities.
Quark is a solid platform for agile teams looking to build a long-term marketing strategy with the help of content marketing. It may not be the best fit for individuals or small digital publishers.
- End-to-end publishing solution for relevant, targeted communication
- Content reuse and repurposing supported
- Rich typography
- Excellent PDF support
- Rich image support
- Training and support
- Minimal system requirements
- Highly responsive end result
- Steep learning curve
- Pricing may be prohibitive for small businesses
- Lack of third-party integration options
Readz
Readz allows publishers to create content and marketing material in the cloud. Organizations looking to connect with large audiences through as many channels as possible should shortlist this platform.
With Readz, businesses can create and publish ebooks, magazines and newsletters to interact with their customers on a daily basis, while also boosting their content marketing efforts through online blogs and pages.
Readz offers two platforms: Readz Publishers and Readz Studio. The first allows magazine publishers to convert their PDFs into flipbooks, while the second enables content creation from scratch.
Publishers can choose one or both according to their needs.
- Built-in business templates
- Adobe InDesign import
- Paywall
- Site embed facility
- Automatically responsive designs
- Drag-and-drop editor
- User interaction tools
- Social sharing
- Enhanced analytics and reporting
- Advanced SEO tools
- Limited design customization options may not meet all users’ needs
- Lack of integration with certain third-party tools
Uberflip
Uberflip is the odd-one-out on this list as it isn’t strictly a digital publishing platform. And yet, it is a valuable tool for digital publishers.
Uberflip is a content experience platform that helps publishers organize their content and then present it to users based on their preferences. Uberflip is best suited for publishers who already have a lot of digital content at their disposal scattered across different formats such as ebooks, blogs, magazines, podcasts, etc., and are looking to increase user engagement.
It helps publishers optimize content use by deploying account-based marketing (ABM), which ensures that content is presented to individual users based on their experience in the sales funnel. Which is why it considers itself to be a digital experience platform.
- Integrates all content from third-party platforms such as YouTube videos, tweets, PDFs
- Offers paywalls
- Integration with marketing tools such as Marketo, Hubspot and Eloqua
- AI content analytics
- Analytics and insights provide valuable data on content strategies
- Helps build personalized experiences for individual users with a few clicks
- Steep learning curve
- Limited SEO capabilities
The digital publishing industry is a fiercely competitive landscape in which participants need to constantly strive for efficiency gains and an operational edge. An online publishing platform can provide analytical tools and marketing features to help publishers gain an operational edge.
The right digital publishing platform can help businesses and individuals to succeed on this front, while also providing analytical tools that help review performance and streamline marketing efforts.
Whether looking to publish content and monetize all on a single platform or via publisher’s own online store, digital publishing platforms provide a number of different routes to market.
As the world of digital publishing continues to evolve, publishers need to keep an eye on their toolkits to make sure they have the best software for the best tools to keep pace with it. For those searching for additional tools that can help publishers organize their content, take a look at our article about the 13 best editorial calendar software for 2024.
FAQs
What Are Examples of Publishing Platforms?
Some popular examples of online publishing platforms, which allow publishers to create, publish, track, and distribute content on the web, are WordPress, MagLoft, Joomag, and Issuu.
What Are the Main Types of Digital Publishing Platforms?
There are several types of digital publishing platforms, including:
- Self-publishing platforms
- Aggregator platforms
- Content management systems
- E-commerce platforms
- Social publishing platforms