News publications are embracing SEO to ensure their stories stand out from the crowd and are seen by as many people as possible.
The rapid pace of internet penetration has seen almost 5 billion people become internet users over the last three decades.1 Audiences now rely more heavily on the internet for information and entertainment, with more than half of Americans preferring to consume news digitally.2
While industry-standard institutions such as The New York Times and Financial Times still run print editions, many publications only have an online presence. Indeed. the proliferation of internet usage between 2000 and 2020 in the US alone caused daily print circulation to drop from 55.7 million copies per day to 24.3 million.3
But it’s not just print media that has moved online. TV news channels such as BBC, CNN and Fox are also focusing on online services in the form of streaming and podcasts.
The proliferation of digital content has seen the average user become reliant on search engines to help find what they need. This has meant SEO now plays an incredibly important role for most news organizations looking to reach new and existing audiences.
Google, for example, claims to send users directly to news sites more than 24 billion times each month, with each referral increasing the odds of a visitor converting to a paying subscriber.4
In this article, we’ll explore what SEO in journalism means and share tips and strategies to optimize content and maximize its visibility.
Table of Contents
What Is SEO in Journalism?
Search engine optimization (SEO) in journalism is a subset of SEO, which has traditionally been the wheelhouse of digital marketing.
Simply put, SEO is the art of optimizing content to rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs). SEO in journalism, meanwhile, is used to help craft stories that readers are interested in, attract audiences based on topics and rank more highly in news SERPs. It is the process of creating content readers want while also making sure they can find it online.
With the abundance of information being shared each day, news providers must first understand their audience’s interests, create content that satisfies those interests and then give the audience a reason to keep coming back.
News sites that want to increase traffic need to consider how they will secure referrals from Google and other search engines. Handling 92% of all online searches, Google is often the first place users go to search for information, including the news.5
But attention spans are short, with about 75% of users failing to scroll past the first page of organic results.6
SEO’s goal then is to ensure that pages rank as close to the top of search results as possible. Ranking outside of those the top results is unlikely to generate traffic, hamstringing revenue goals in the process.
Although it may seem daunting to rank in such a competitive environment, it’s not impossible if publications understand some SEO basics.
What Are the Benefits of SEO for Journalists?
The digital transition has opened the door to a proliferation of media and news outlets of all sizes and focus.
In an increasingly competitive market, news websites can use SEO to benefit in four main ways:
1. Gain Greater Visibility
The position a story achieves on a SERP influences how many visits they will receive.
Most people trust Google’s algorithm to understand their search intent and return a relevant article that provides the best answer to their question or keyword.
That’s why ranking as close to the top is important, as most users will not scroll past or focus on anything but the first few results.
2. Generate Organic Traffic
Greater visibility is the first step towards attracting more traffic. The first few organic SERP results generate the bulk of organic website traffic for a keyword and this traffic is “free” in the sense it does not require the use of pay-per-click (PPC) search ads.
On average, the first organic result on Google averages a click-through rate (CTR) of 38.9%, but this value drops to just 1.5% for the 10th ranked result.7 Links that rank on any subsequent SERPs are unlikely to be seen by the overwhelming majority of users.
3. Opportunity for Monetization
A properly optimized site has a greater chance of attracting more visitors, which in turn creates new opportunities for monetization.
The most common methods include selling ad inventory and/or putting content behind a paywall. However, some publications are producing listicle articles with affiliate links or are focusing on eCommerce merch sales.
The New York Times’ Wirecutter review section, for example, engages in affiliate marketing.8 The section produces detailed guides and roundups to help readers make informed purchases. Each article contains links to the items discussed and the NYT receives a commission.4. Become a Trusted Source
Trust is everything in journalism.
With fake news an issue, users expect Google to filter search results and show only reliable content and news websites.
One of the quickest ways to gain trust is to rank consistently or feature on the Google News platform.
One effective method to cement trustworthiness is to create professional content, partner with already trusted brands when possible, and consistently rank on SERPs or feature on Google News.
Why Google News Matters and Why Newsrooms Should Use It
While Google Search and Google News are often mixed up, it’s important to understand they are not the same thing.
Although Search and Google News use the same algorithm, Google News has its own unique ranking signals, including clicks, publication authority and content freshness.
Launched in 2002, Google News helps users find content and news sites that publish timely and topical stories. While Google News displays keyword-driven results it also allows for content discovery based on personalized interests and location.
If a search query is linked to a current event, Google shows a prominently placed Top Stories carousel above both organic search engine results and search ads.9
Google’s algorithm serves as the gatekeeper and as long as publishers meet the search giant’s guidelines, such as providing original content and limiting advertising, and implement sound SEO practices then they will be better positioned to rank on Google News.10
There are other perks of appearing in Google News results, such as being better placed to negotiate a deal with the search giant for inclusion in the Google News Showcase program.11
14 Essential SEO Tips for the Newsroom
Even though Google News SEO is a niche discipline, the same strategies used for Search are applicable.12
SEO strategies can be divided into three key categories: on-page, technical and off-page SEO.
On-page SEO is the practice of optimizing elements on a website to improve rank, while off-page SEO refers to actions that build a publication’s trustworthiness and authority. Technical SEO, meanwhile, refers to optimizations that help search engines crawl and index a site.
Not only are the top-ranked results optimized for on-page, off-page and technical SEO, Google is constantly tweaking how its algorithm determines ranking, so editors must be able to adapt.
To help publications stay on top of Google, we’ve compiled a list of essential SEO tips for any newsroom.
We’ve grouped the tips in order of relevance to the various roles found within a newsroom. After all, journalists, editors and publishers each have their own responsibilities for their news website.
Tips for Journalists
On-Page Factors
1. Write Snappy Headlines and Titles
Similar to humans who look at headlines to determine what a story is about, Google’s algorithm looks at the H1 tag and meta title to understand its relevance. These words influence how search engines rank content.
Optimize headlines and title tags for clarity and include keywords to increase click-throughs. But be careful to avoid writing lengthy headlines and titles, or stuffing them with keywords.
Google will truncate lengthy titles to fit the SERP, which could leave users guessing as to the page’s content. The general guideline is for headlines not to exceed 60-70 characters.
Keyword stuffing, meanwhile, might encourage Google just to create its own title for a page.13
2. Be Original
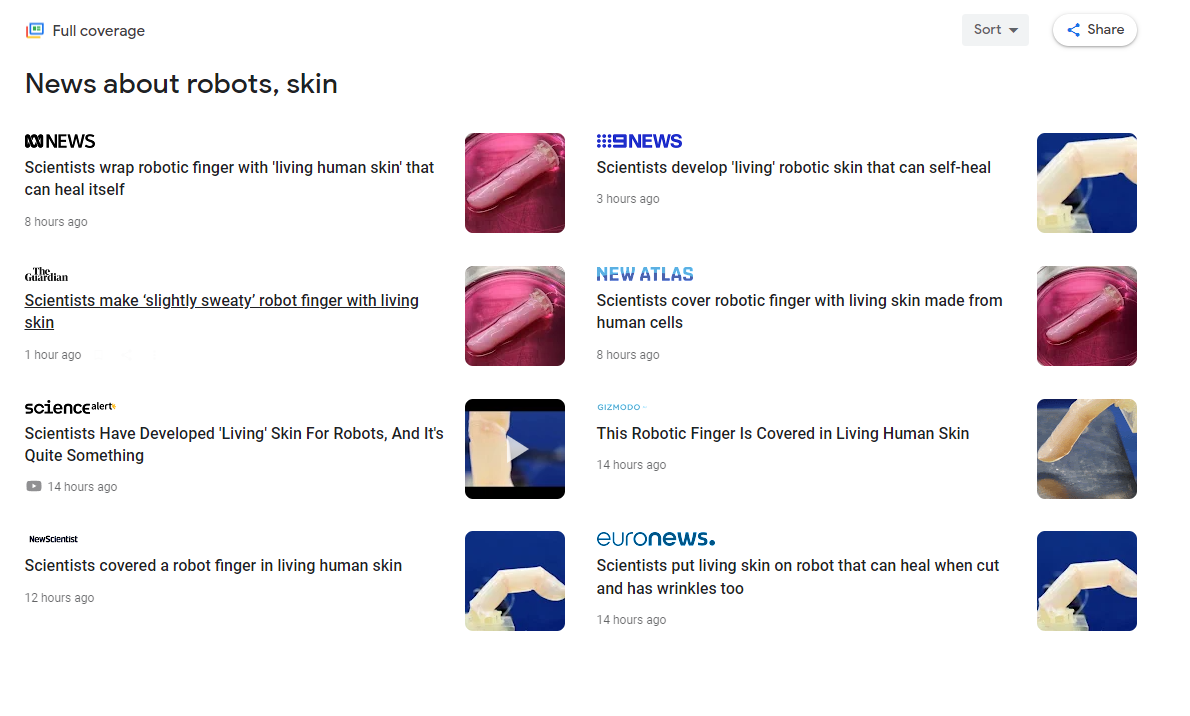
Google News rewards publications that are first to cover breaking news.
The homepage of Google News features the latest relevant stories. A keyword search for a topic of interest will return content that is anywhere from a few hours to days old and wrapped in rich text to draw readers’ attention and boost click-through rates (CTRs).
There are ways to increase the likelihood of pages’ ranking higher.
First, establish a reporting schedule. Publish regularly and provide new information with each story to signal consistency to search engines.
Although the ability to create content quickly is important — when it comes to breaking news this is measured in minutes not hours — this factor shouldn’t be all that a publication relies on.
Dedicate some time to creating a strategy based on an understanding of readers’ behavior and focus on quality content. A good place to start is on SERPs.
Keyword Research
Keyword research helps journalists understand what users are searching and use that information to create stories.
What’s currently ranking for a keyword? Has there been a rising interest in that term? Answers to these questions should serve as a guide to present stories with a unique angle.
For example, FiveThirtyEight runs an interactive NFL predictor every year that is updated after each game to keep users engaged.14
If there is uncertainty over what keywords a target audience is searching, creating valuable content is a difficult task. Blind content creation is unlikely to appeal to users or lead to clicks despite all other optimization efforts.
3. Figure Out Users’ Search Terms
Unlike traditional SEO, journalism is rarely just one story in isolation.
While it’s still necessary to look at the search volume and keyword difficulty when picking a topic, it’s more important that publications understand if a term indicates if users are wanting to learn about a specific theme as this plays a role in engagement.
To determine relevant keywords to focus on, there’s no shortage of SEO tools. Some free keyword tools include:
These platforms provide data on the popularity of target keywords.
When a keyword is chosen, publications should adopt a pillar and cluster approach for content creation.19
Pillar and Cluster
Start by crafting content based on a broad news topic (pillar) and use it as a base to craft a series of clusters or specific content that links back to the pillar.
For example, a publication may choose to focus on upcoming Olympics as their pillar content and follow it up by a series of posts about the athletes taking part, the most interesting matchups or key rivalries.
The general rule of thumb is that publications that are already established or have authority in the eyes of Google are more likely to rank for very broad and competitive keywords while their less established counterparts will fare better for more specific or long-tail keywords.
4. Don’t Ignore Evergreen or Seasonal Keywords
Evergreen keywords are topics that readers will always be interested in and keep coming back to time and time again. These articles make for a great source of constant traffic.
For example, a sports publication might create a list of championship basketball teams over a 20-year-period to provide value.
Taking this a step further, the same publisher could link to this post in the future when another final is around the corner for a boost in engagement.
Similar to evergreen ideas, seasonal keywords are also a great way to capture traffic at unique timepoints in the year.
Holidays such as Valentine’s Day or Christmas are great examples of when time-sensitive content can shine.
5. Follow the Trends
Google Trends is a useful tool for journalists, as it provides data on the popularity of specific keywords and interests over time.
Being able to see into the mind of audiences gives journalists the ability to create content that appeals and drives engagement. The tool gives journalists unique insights into keywords that may have little to no competition in the present, but have the potential to be a future driver of traffic.
Being present with content at this early stage can help publications go viral and help cement their expertise and authority.
Tips for Editors
In addition to the above tips, editors have a range of other practices they need to keep in mind when editing, writing or assigning projects.
On-Page Factors
6. Keep Content Up-To-Date
Content freshness, or how recently a story was published, also impacts rankings. As news breaks, a search engine will promote up-to-date content to the top.
If writing new articles in time is not a possibility, consider updating older ones on the same topic.
However, make sure to follow the inverted pyramid structure. New information should feature on the top of the page with everything else pushed to the bottom.
Also, be careful not to overuse or duplicate content from other places or even internally as Google can lower rankings if it senses intentional manipulation. In case of internal content reuse,20 there is no penalty but it does limit control over which page ranks for that keyword — this is known as keyword cannibalization.21
7. Don’t Forget Bylines
To ensure transparency, Google suggests news portals provide bylines with each story.22 Although not an absolute requirement, including a byline with each story does increase the odds of ranking.
Besides helping combat misinformation, this also helps authors showcase their expertise and build authority in their niche.

Be sure to include at least the name, picture and a short writer bio in each story. Another option is to link to an author page that contains the writer’s information.8. Label Images
Images provide a deeper understanding of the story to users.
But Google can’t understand an image unless explicitly told through alt text, captions, and image URLs that describe its contents.
Besides labeling images properly, make sure to compress them as well so pages load faster, which in turn helps search engines crawl and index faster.
Technical SEO
9. Link Internally
Internal links connect one page of a site to another. Besides helping users navigate to different pages on a site, these links are important ranking factors as they also help search engines understand site structure.23
Two common ways to implement them are navigational or contextual links. Navigational links are hyperlinks added to the footer, header or sidebar of a page while contextual links are placed within the body of text.
10. Focus on Core Web Vitals
Mobile friendliness, or the optimization of pages for smartphones, is an important factor to consider.
With mobile devices responsible for 54.4% of all traffic by the end of 2021, Google’s algorithm now favors mobile-friendly sites above all else.24
In fact, Google developed its own set of criteria known as core web vitals (CWV) to help it determine user experience on websites.25 Factors it considers include page speed and mobile-friendliness.
As such, editors should optimize their content for smartphones. Use short sentences and paragraphs to make text skimmable and improve readability on smaller devices.
Content from our partners
At a website-level, publishers should explore ways to make a light-weight version of their site, including Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP).
While Google removed restrictions that prevented non-AMP sites from ranking as featured snippets on Search in 2021, AMP remains a viable option of improving user experience on mobile.26
Tips for Publishers
Technical SEO
11. Don’t Complicate Site Design
Google rewards websites that are easy for users to navigate and read.
Since the nature of the news cycle is time-sensitive, most users care about how relevant and informative website content is rather than the site’s appearance.
There’s no need to complicate a website’s architecture. A basic and clean structure which includes a headline, image and date, followed by the actual content is generally enough to satisfy Google’s algorithm.
12. Help Google’s Crawl Bot Do Its Job
Google uses crawl bots to constantly scour the web for new websites and content while also checking already crawled sites for updates.
To feature on Google’s SERPs, websites have to be crawled and indexed first.27
Crawling helps Google’s algorithm determine the relevance of content for a keyword and better understand the relationship between pages on a website.
Be sure to group content into broad themes using tags and categories so that the site is accessible and logical for users and search engines. Internal links also help crawl bots by letting them know which article is important on a site.
To gain a deeper understanding of how users are engaging with a site and find weaknesses in design, use Google Analytics to understand user behavior and diagnose issues.
13. Create an XML or HTML Sitemap
For news sites with many articles, an XML sitemap or a blueprint of the site is an important ranking factor.
Sitemaps are a separate file uploaded to Google Search Console. It should contain a link of all the pages to be crawled to help Google index pages faster.28
Alternatively, HTML sitemaps are another option. These are links to other sections of a news portal commonly seen at the bottom of each page or the footer that improve user experience by reducing the number of clicks in navigation.
While both types of sitemaps help improve rankings, XML sitemaps are only meant for crawlers while a HTML sitemap benefits both users and crawlers.
Off-Page Factors
14. Build Backlinks
Backlinks are links that point from site A to site B and are an integral part of SEO.
Such links indicate to Google that site B’s content carries authority. Essentially, when someone else links to content elsewhere, it boosts that site’s credibility and is a vote of confidence for it.
It’s entirely possible for websites to garner backlinks organically, and is a common occurrence for larger, more established and respected media outlets.
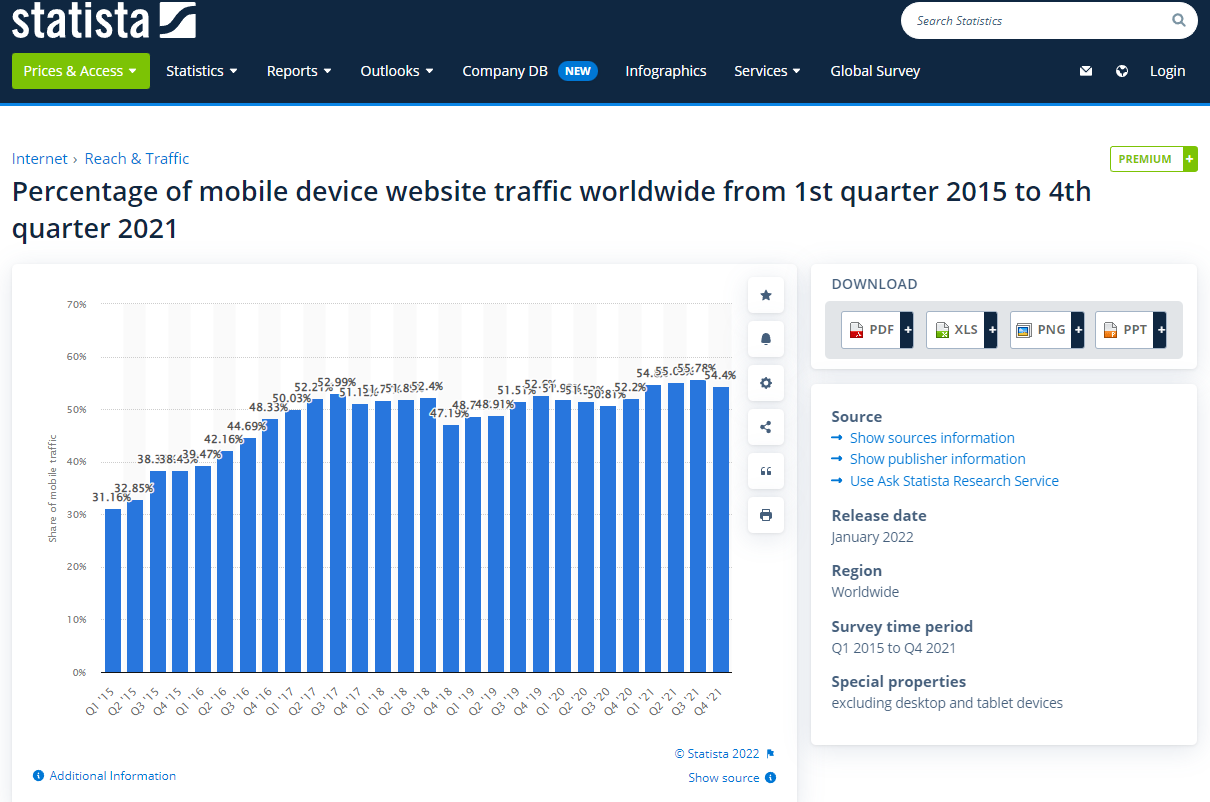
One method to generate backlinks is to craft high-quality original content, especially data-driven content such as interactive infographics. An example of an organic backlinks can be seen further up this page, where we linked to Statista’s graph on mobile device website traffic.
Alternatively, some publications may choose to focus on content syndication.29 This is a great way to build link juice as third-party websites must link to the original source.
Lastly, establishing strong relationships with other journalists can pay off in the long run as it can lead to links and references.
But be extremely careful. Engaging in practices such as trading or buying and selling links violate Google’s quality guidelines and can tank rankings or even lead to a site being delisted.30
Final Thoughts
Journalism is evolving as user habits change.
Writing stories based on keywords and topics searched on Google should now be considered a core journalism strategy.
Rather than dismiss SEO strategy as too technical or writing for robots, journalists need to embrace it as a way to push their stories and site in front of a larger audience.
With information easier to access than ever, it’s the publisher’s responsibility to use available tools to figure out what people want and give it to them fast.
Beyond access to a bigger audience, being part of the Google ecosystem can lead to potential financial benefits for publishers as the search engine is investing in quality journalism.
At the end of the day, it is the journalists and publishers who adapt today that will reap the rewards tomorrow.
- Internet users in the world 2022 | Statista
- More than eight-in-ten Americans get news from digital devices
- Trends and Facts on Newspapers | State of the News Media | Pew Research Center
- Setting the record straight on news
- Search Engine Market Share Worldwide | Statcounter Global Stats
- How To Optimize Your SEO Results Through Content Creation.
- Google Organic CTR History – Advanced Web Ranking
- Wirecutter: New Product Reviews, Deals, and Buying Advice
- Google Top Stories Carousel – State of Digital Publishing
- Google News policies – Publisher Center Help
- Google News Showcase Remains Under Pressure to Do More
- Google News SEO: 2022 Edition | State of Digital Publishing
- An update to how we generate web page titles | Google Search Central Blog
- 2021 NFL Predictions | FiveThirtyEight
- Use Keyword Planner – Google Ads Help
- Google Trends
- Keyword.io
- Keyword Explorer – SEO Keyword Research Tool [Free & Pro] – Moz
- Content Cluster Strategy Toolkit | State of Digital Publishing
- Avoid Duplicate Content | Google Search Central | Documentation
- What is keyword cannibalization? • Yoast
- Google News policies – Publisher Center Help
- Importance of link architecture | Google Search Central Blog
- • Mobile percentage of website traffic 2021 | Statista
- Core Web Vitals report – Search Console Help
- AMP SEO: A Guide for Publishers
- Google Crawl Budget: A Publisher’s Guide
- Build and Submit a Sitemap | Google Search Central | Documentation
- Content Syndication SEO Best Practices | State of Digital Publishing
- Link Schemes | Google Search Central | Documentation












